‘gparted’ is the graphical version of ‘parted’ and is the tool to use to resize the main partition used for raspbian (or you could use use parted if you prefer the command line of course!). It can also be used to check and repair a SD card disk.

To do this you’ll need to put the SD card you want to work on in a USB to SD card adaptor and boot your RPi from a separate SD card. If you’d rather use a windows tool we’ve found that gparted just works whereas all of the windows based partition managers we tried don’t, so better to just get over the hassle factor and use the RPi to do this if you don’t have a separate Linux system.
Installing gparted on the separate Raspbian SD card that will perform the change

From the command line use:
How to Remove a Hard Drive Partition Using Gparted. If an operating system installation should fail you must remove the partition with the failed operating system. This will give room to try to install the operating system again. Gparted can be installed on most popular Linux distros including Ubuntu, Fedora, Arch Linux, and their derivatives. It can help you create and resize partitions easily. So to do that, you'll need the Live USB version of GParted. Apart from that, the Live USB version or the installable versions are very much the same things.
Apr 25, 2009 GParted - Introduction GParted is one of the most popular partitioning software. It comes included with most modern Linux distributions. It also ships in a large number of dedicated rescue & recovery distributions. To name a few distributions that come with GParted: Ubuntu, Linux Mint, PCLinuxOS, Wolvix, and others.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
sudo apt-get install gparted
Running gparted
To run it use ‘sudo startx’ to load the GUI as gparted needs root user privileges
Then from the start menu select run and enter ‘gparted’
Resizing Your Main Partition
From the top bar devices drop down select “dev/sda” (or whatever your external USB adaptor has been called).
Gparted For Windows
Right click somewhere on the graphic and select ‘unmount’ first as operations can’t be carried out on a mounted partition.
Right click the main ‘ext4’ partition and select ‘check’, then click the green tick and let it check the partition for you (this isn’t essential but its a good idea as if there are issues it will likely cause the resize to fail).
Right click the main ‘ext4’ partition and select ‘resize’ then enter the new size you want it to be.
Right click the main ‘ext4’ partition and select ‘check’ (we’ve found this to be necessary to ensure the new partition size is correctly updated in the file system even though it should be done as part of the resize – kept us chasing constantly failed resizes for hours before we discovered this).
Finally click the green arrow button to carry out the changes.
Reboot the RPi (yep its stupid but we’ve found a reboot to be needed even after removing and re-inserting the SD card), sudo startx, run gparted, select the USB drive and check the ext4 partition is locked again (mounted) and has its boot string back.
Install Gparted Partition Manager in Ubuntu via terminal and Ubuntu Software Center
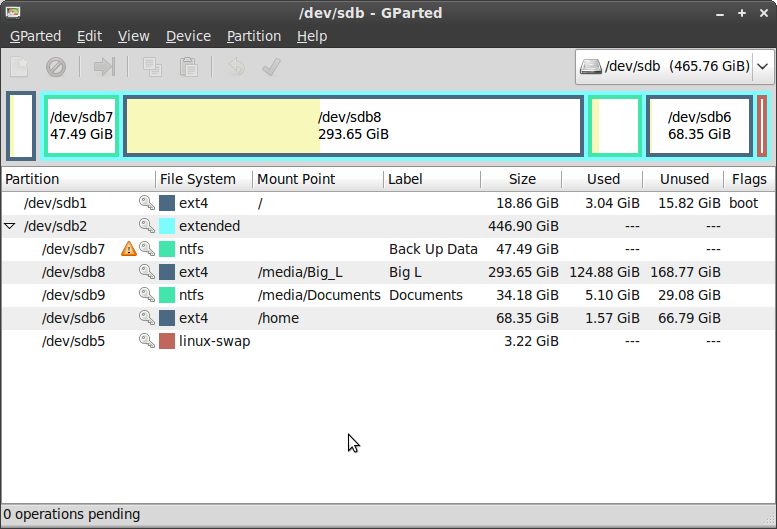
Gparted a free open source software for graphically managing the hard disks. With live Gparted on a bootable pen drive you can copy, label, resize and move partition without loss of data. It can also rescue data from lost partitions. Gparted can work with or create ext2, ext3, ext4, fat16, fat32, hfs, hfs+, linux-swap, lvm2 pv, nilfs2, ntfs, reiserfs, reiser4,ufs and xfs formats.
Gparted is the one of the best hard disk management software for Ubuntu and Linux Base Derivatives. There is two method to use it. You can install it on the system or can create a bootable pen drive with the ISO file of the Gparted.
installation of Gparted in a Ubuntu-Debian system
- 1. Via Terminal
- 2. Via Ubuntu Software Manager
1. Via Terminal
Open the terminal via “Ctrl+Alt+T” and run the command below.
2. Via Ubuntu Software Manager
Open the Ubuntu Software Manager and search Gparted. It will search the Gparted. Now click “Install” to install the Gparted.
Creating a Live Bootable Pen Drive with Gparted ISO
First download Gparted ISO from the link below
Gparted Resize Partition
Now read the posts to create the gparted bootable pen drive in windows and linux via clicking the link below

Gparted Ui
Gparted Download
Comments are closed.